How things work¶
It is full-week intensive work.
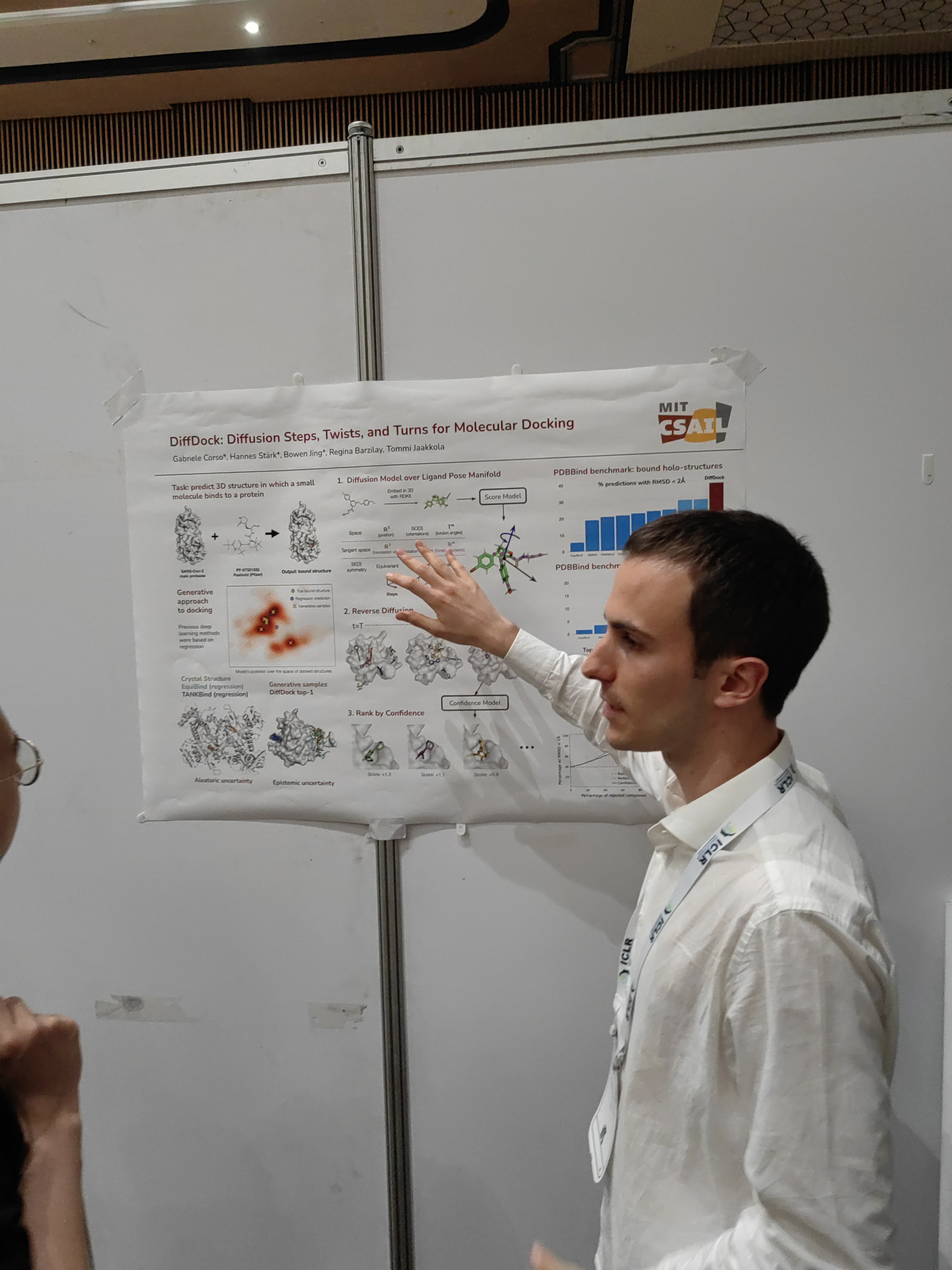
There are talks, but most interesting (besides networking) are poster sessions.


ICLR -- International Conference on Learning Representations, one of the most important A* conferences.
Started in 2013.
Numbers of 2023: 4,966 total submissions, 1574 accepted (32%).
Statistics: https://guoqiangwei.xyz/iclr2023_stats/iclr2023_submissions.html
Paper submission deadline: 21 September 2022.
Reviews released: 5 November 2022
Acceptance notification: 21 January 2023
Each paper receives at least 3 reviews, then Area Chair writes 'meta-review', Senior Area Chair confirms it and finally --- Program Chairs release the decision.
First time in Africa. Should have been in Addis-Abbaba in 2020, got cancelled.
Now it was in Kigali, Rwanda.
First offline ICLR conference since pandemic!
The location was a modern convention center.
It is full-week intensive work.
There are talks, but most interesting (besides networking) are poster sessions.


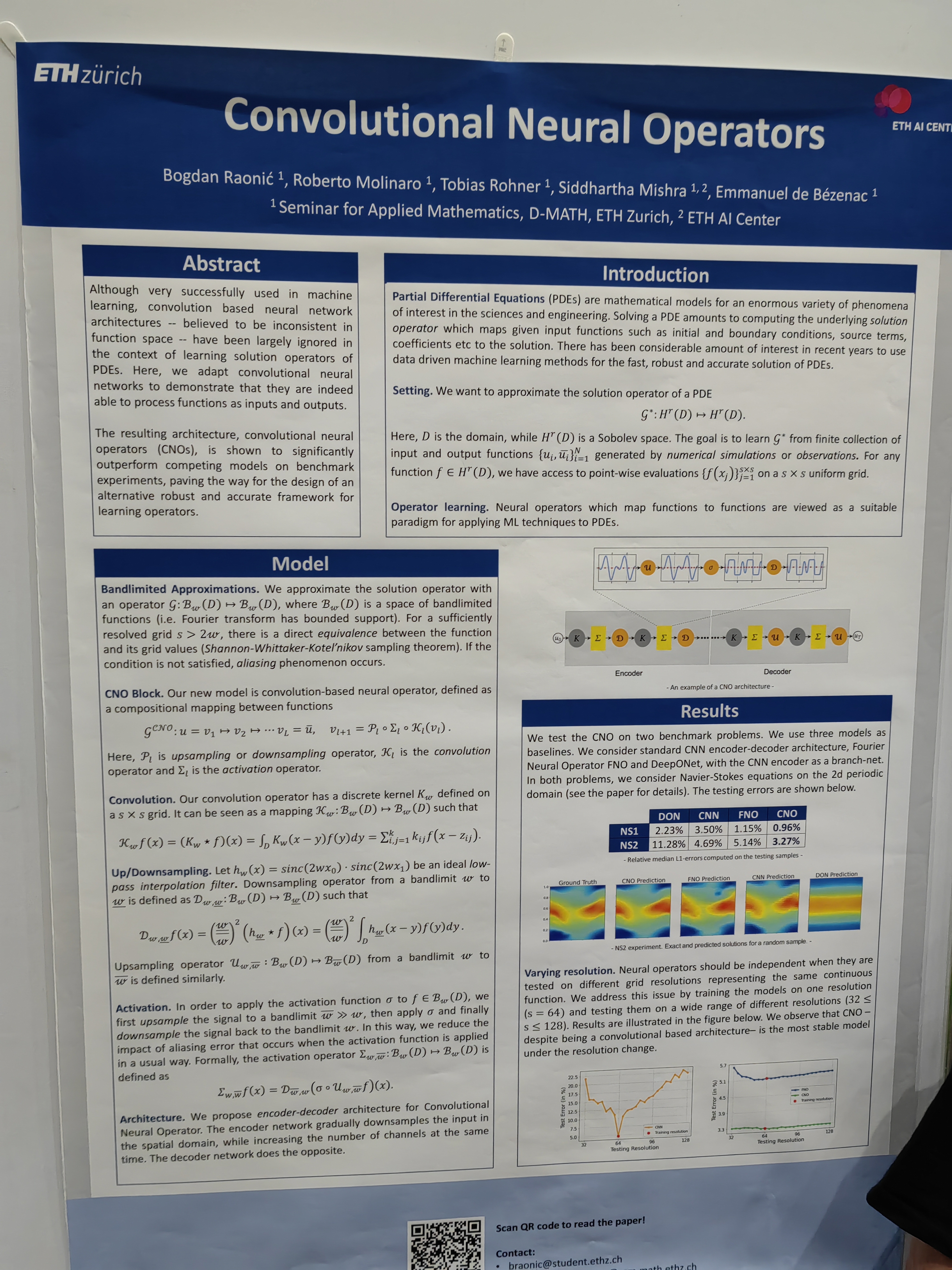

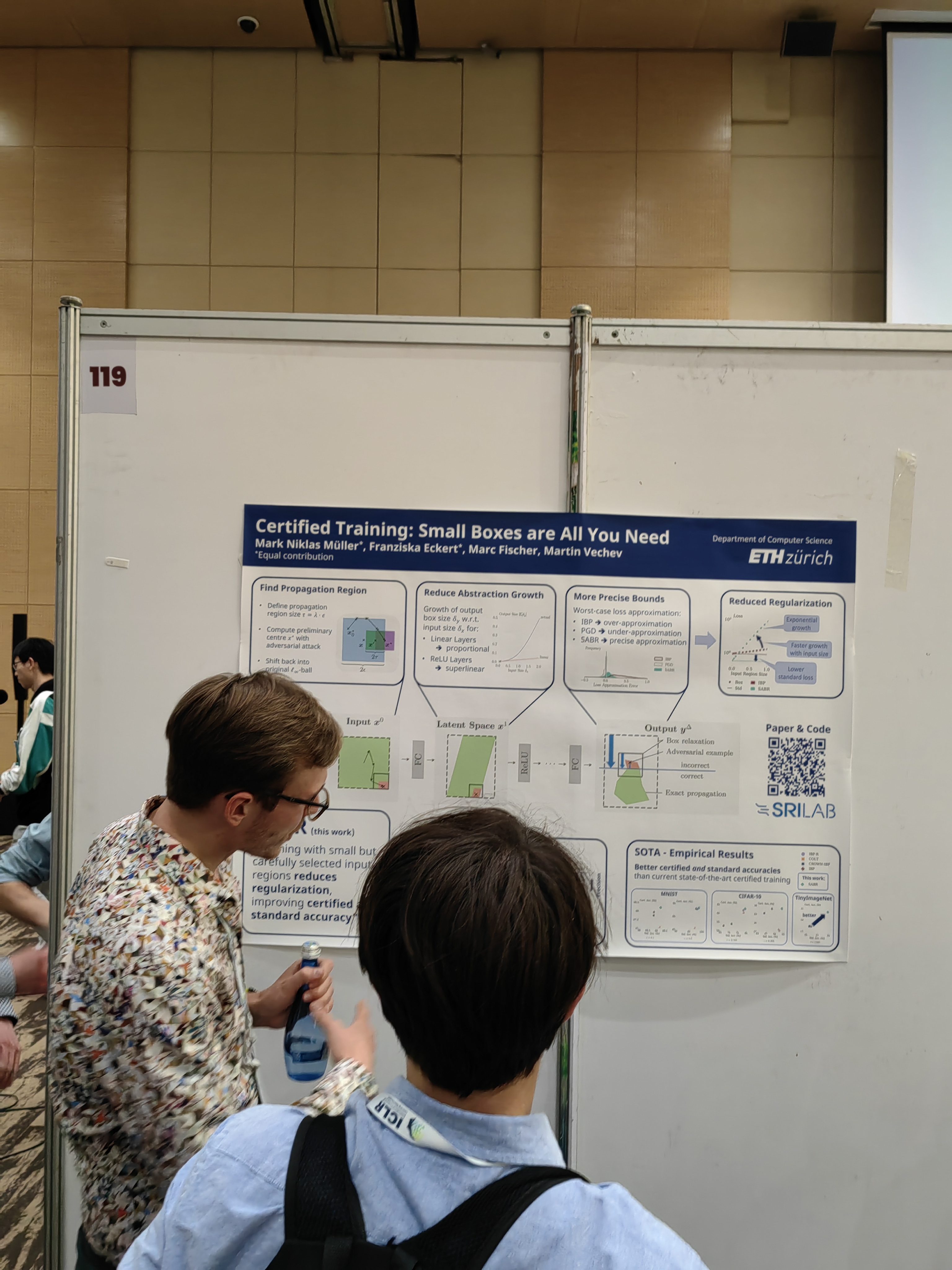
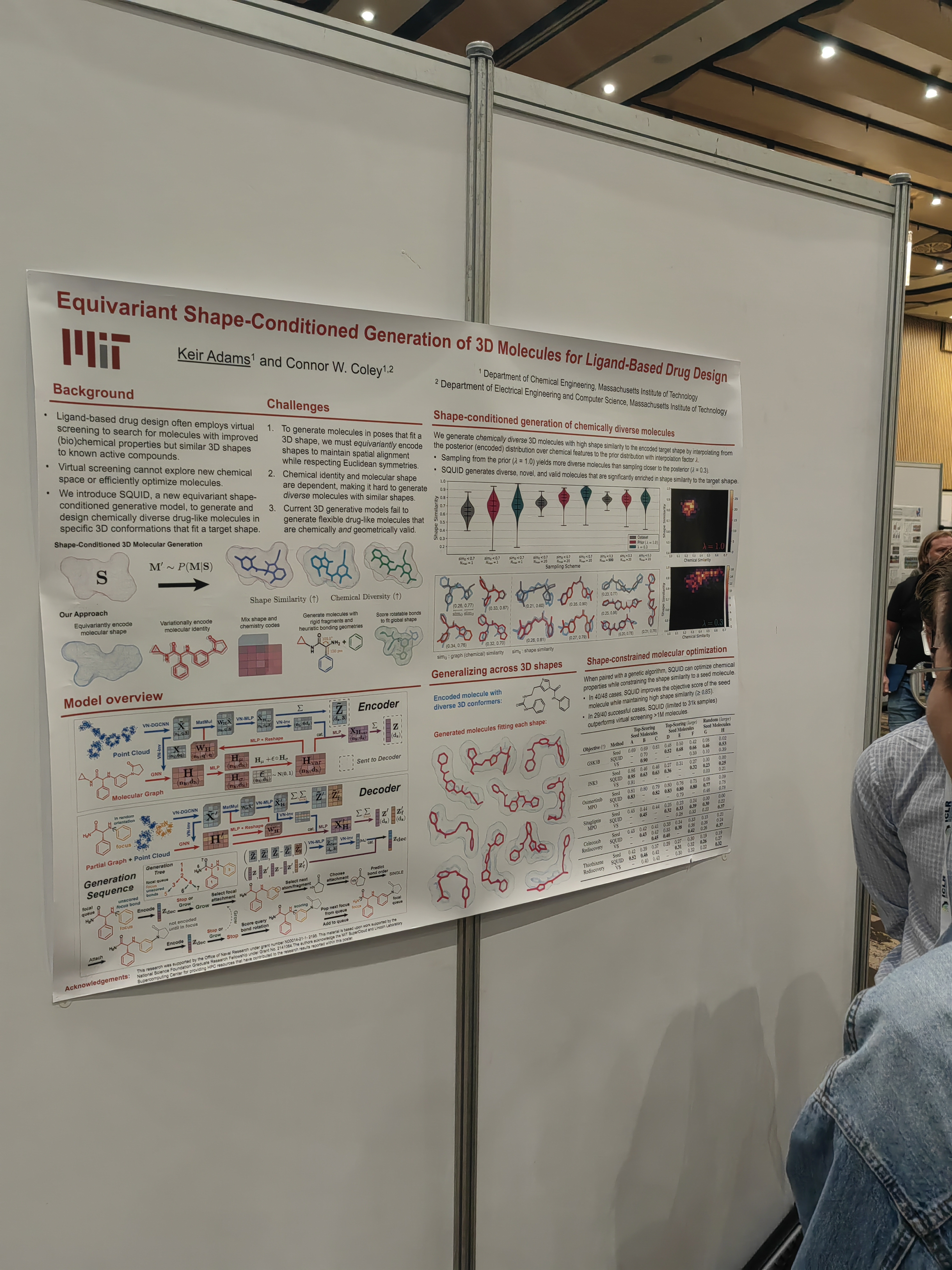
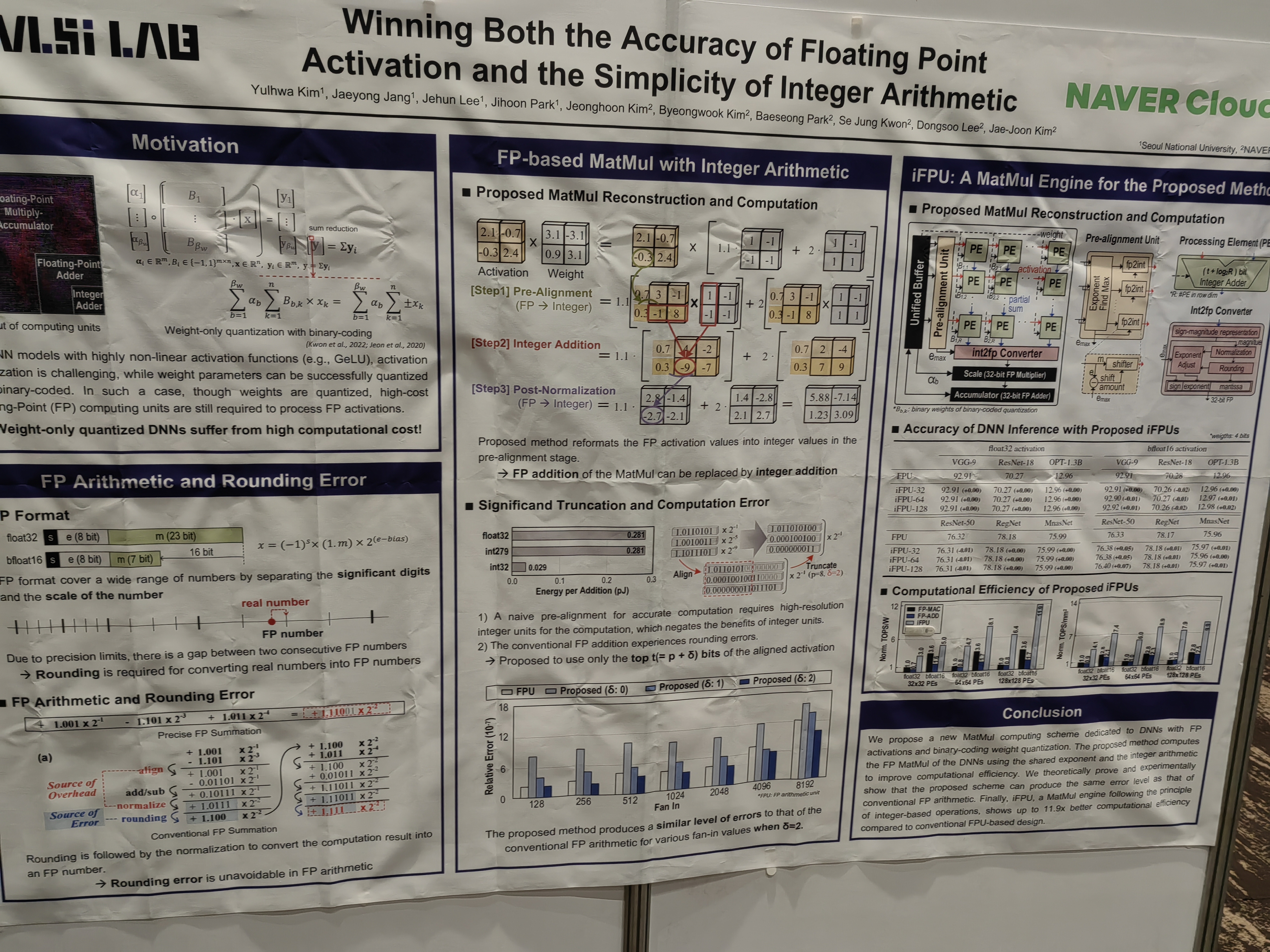
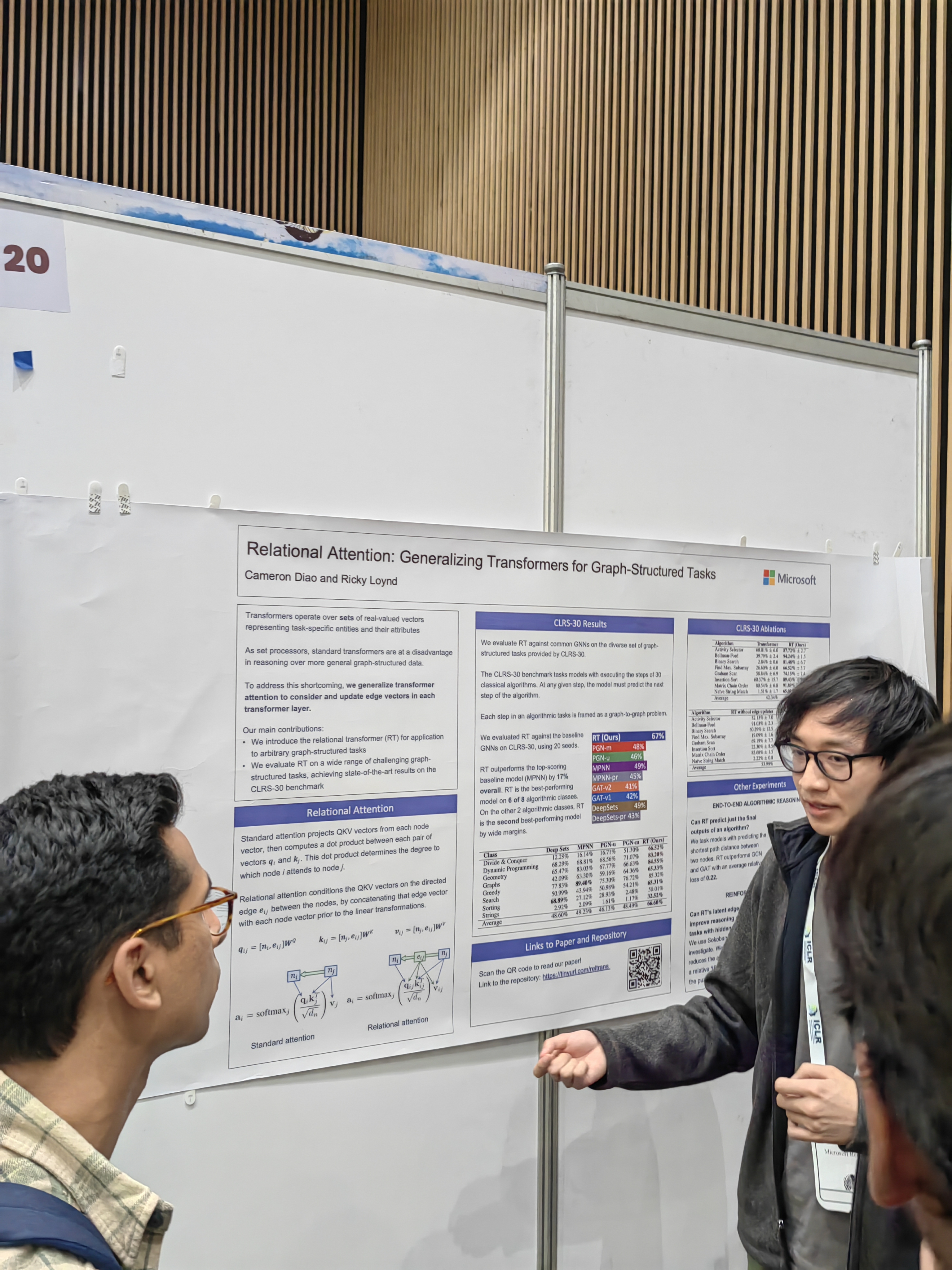
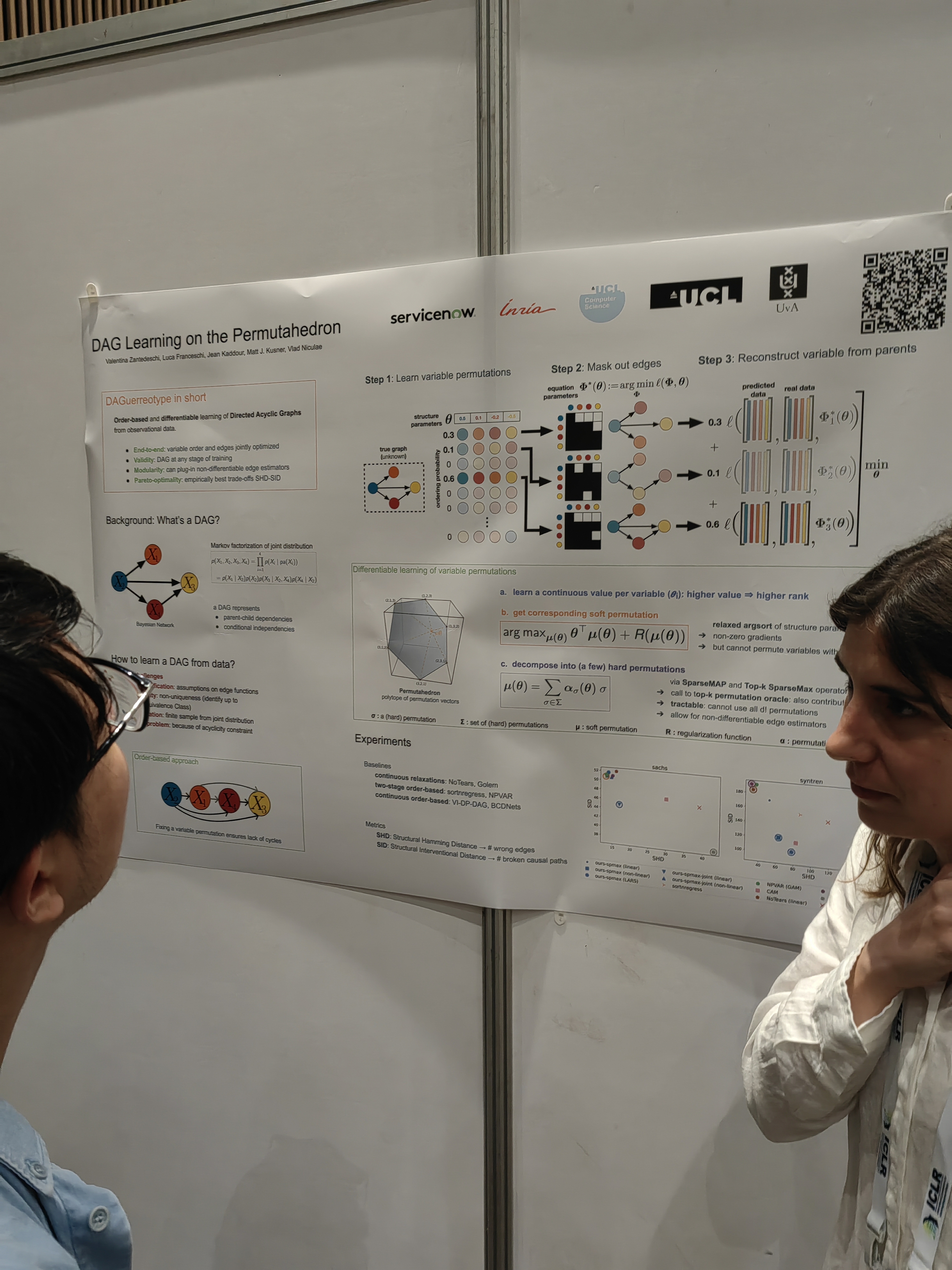
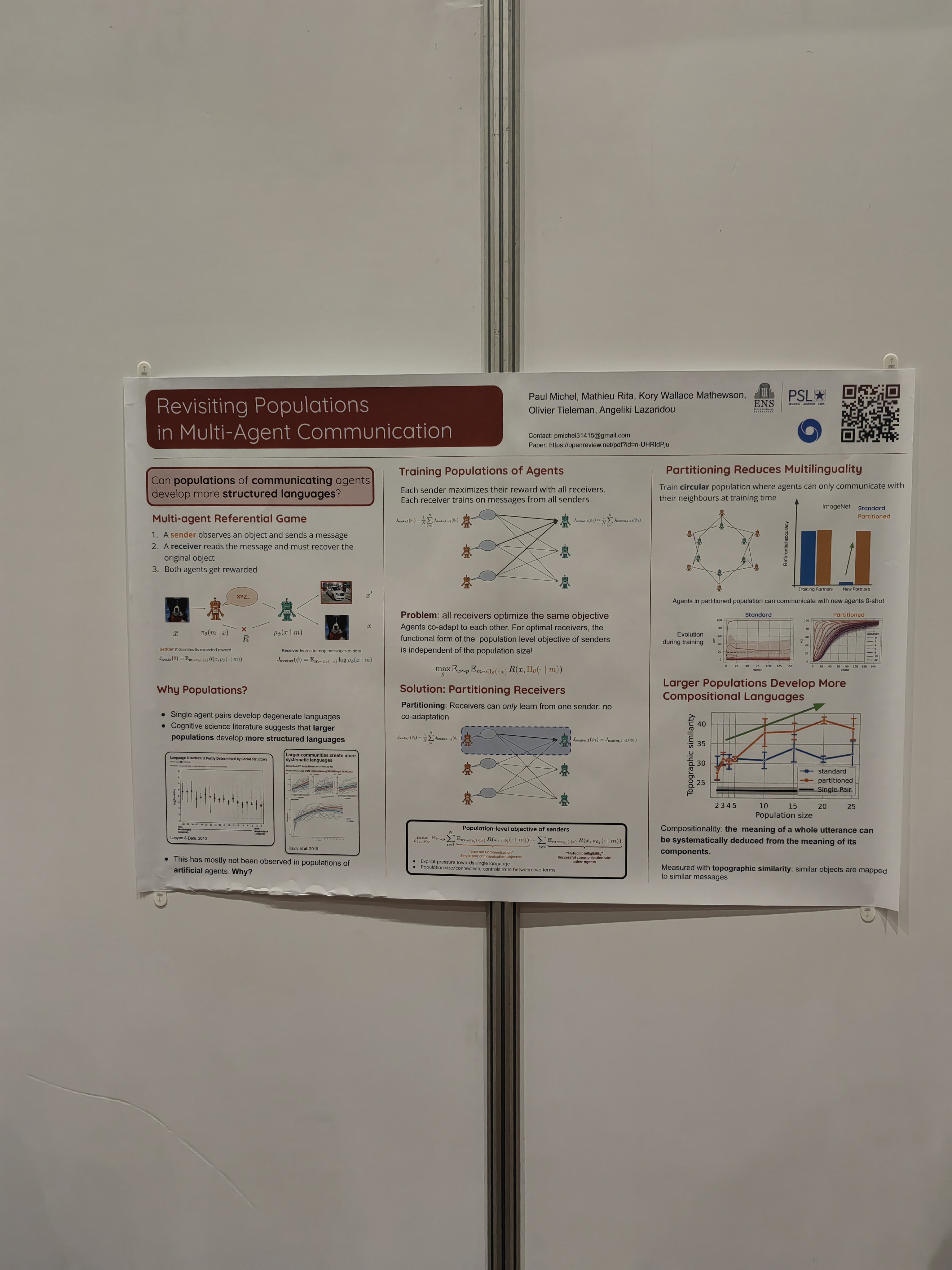
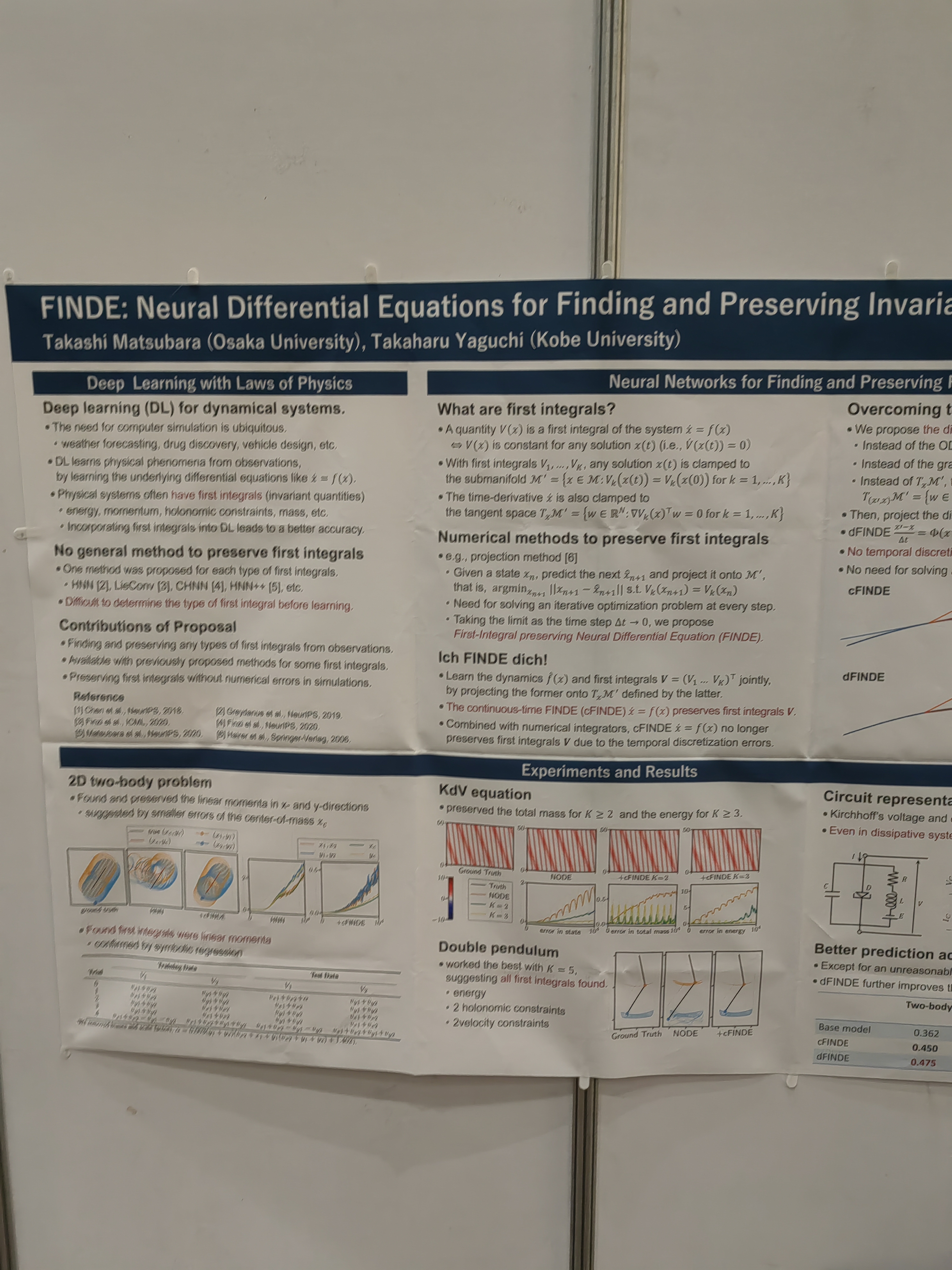
This papers learns the system from trajectories with learned invariants as well.
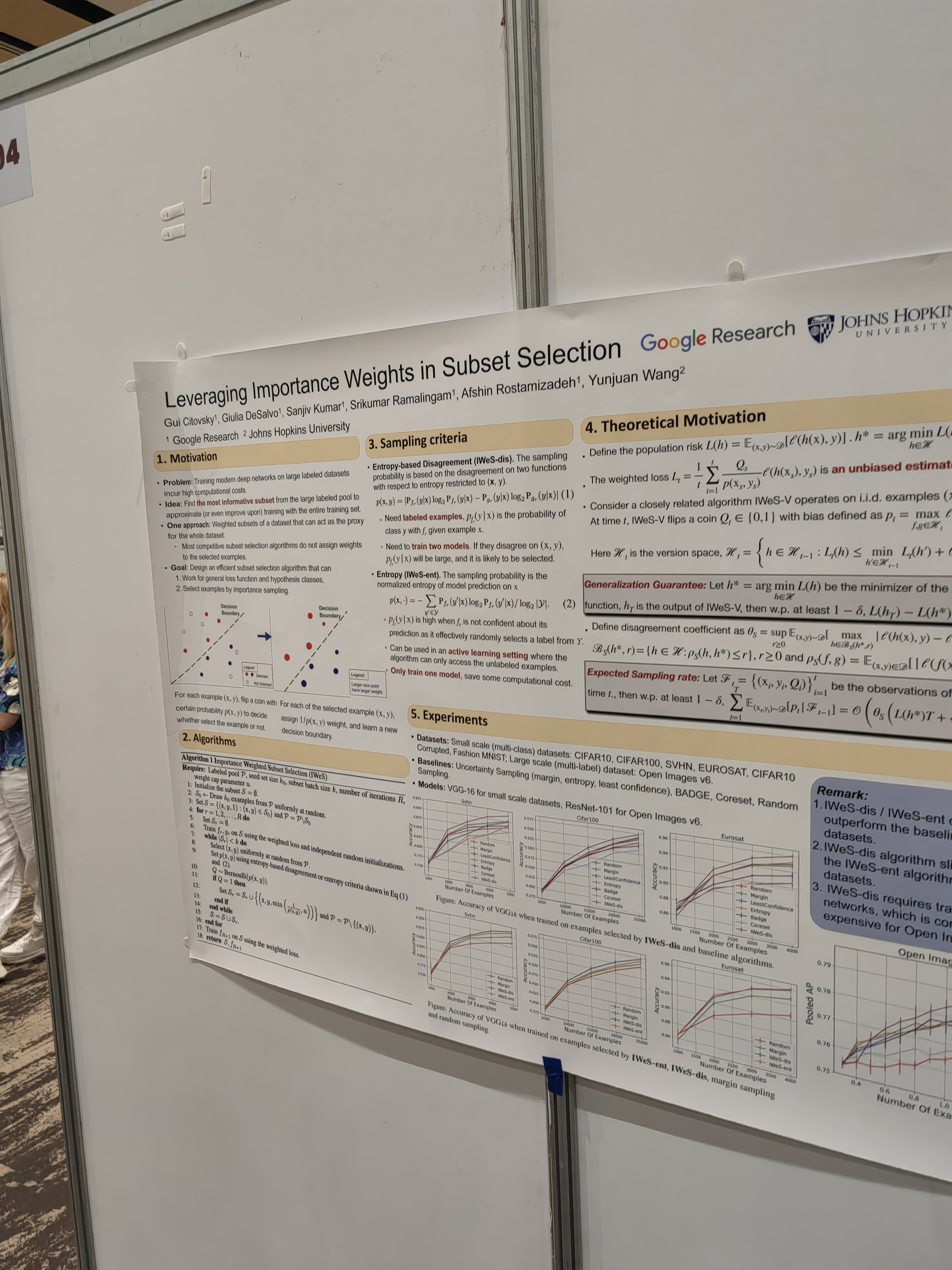
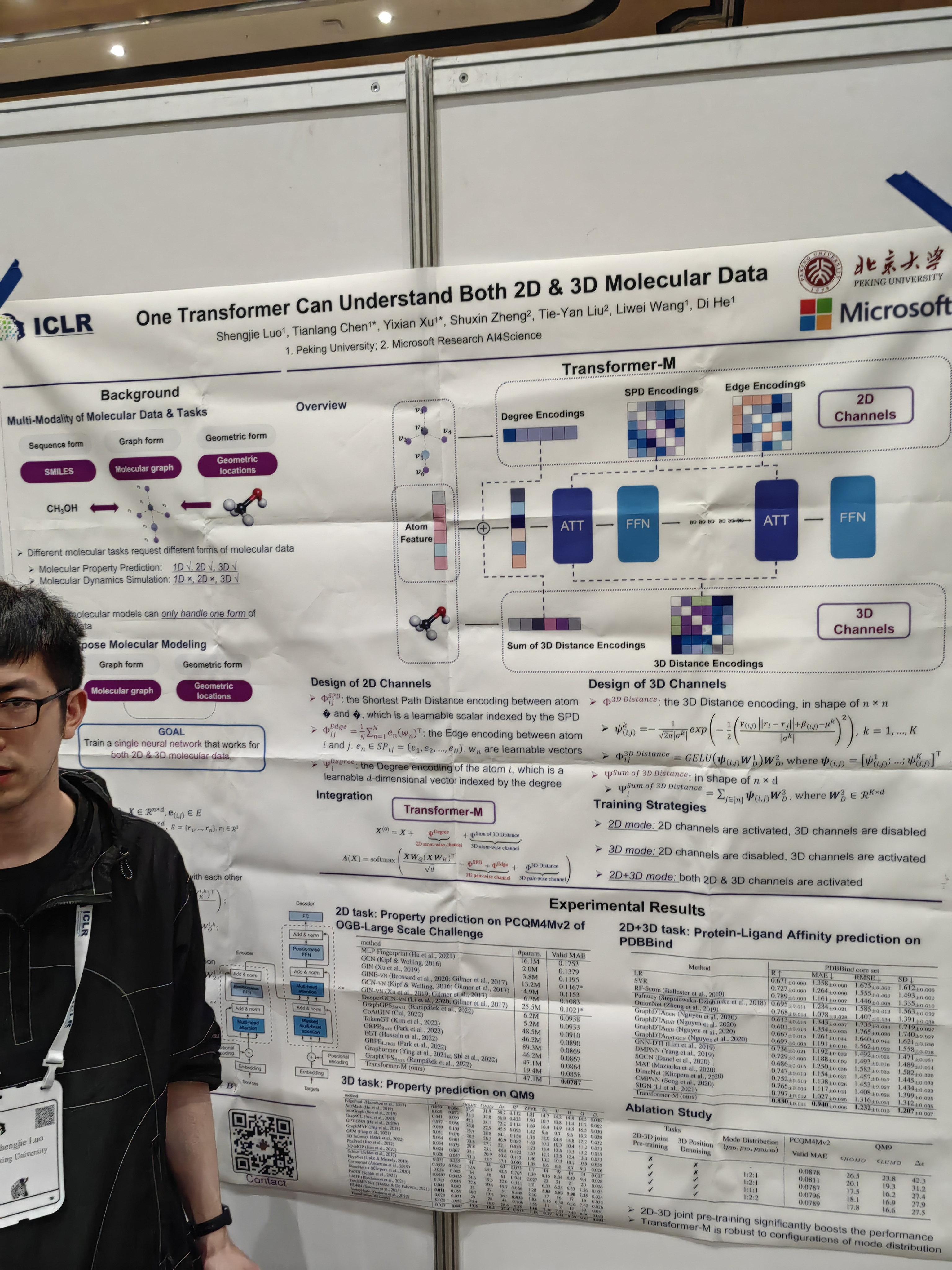
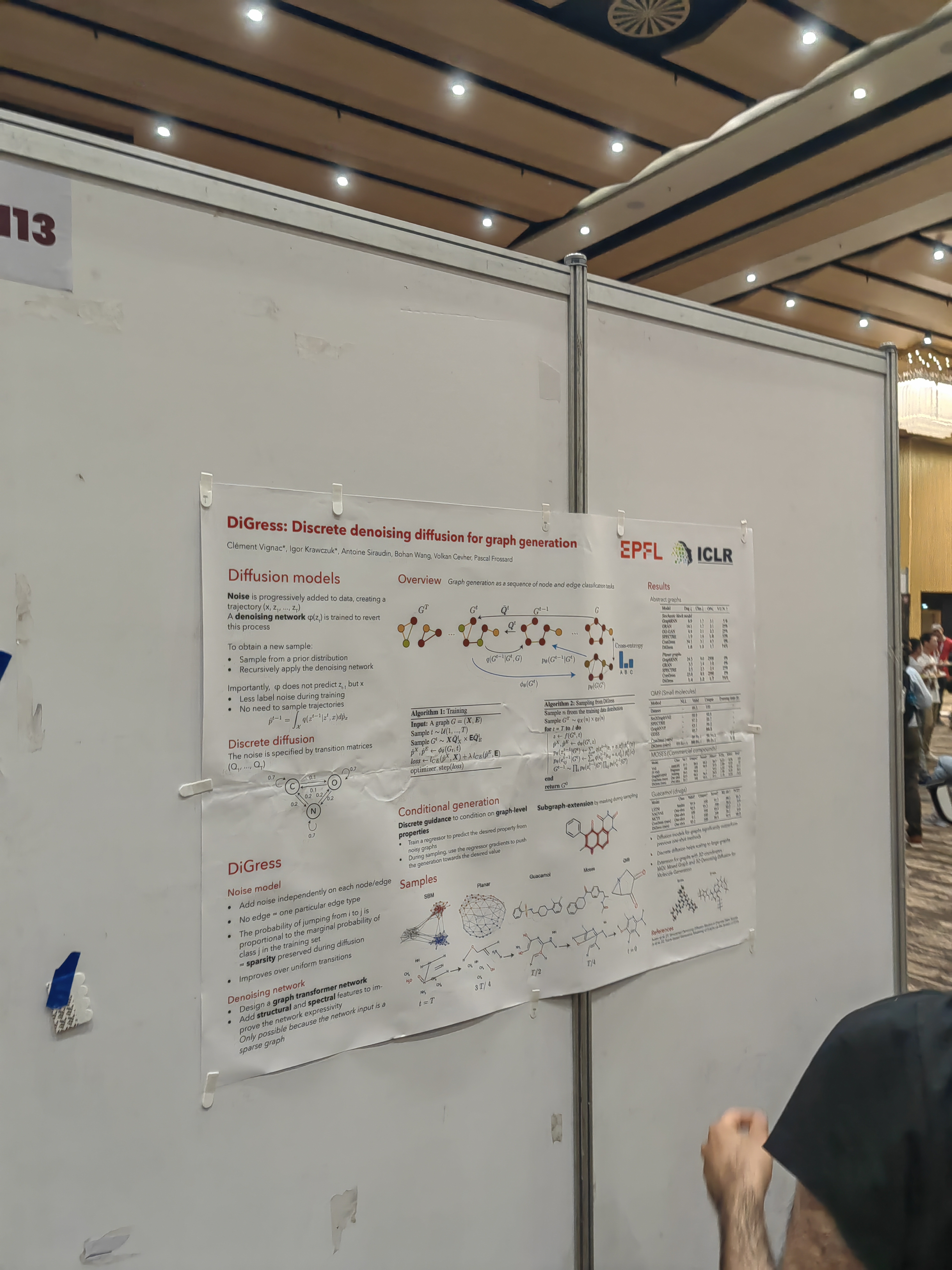
Idea: try to make artificial data by learning the instruction from the result.
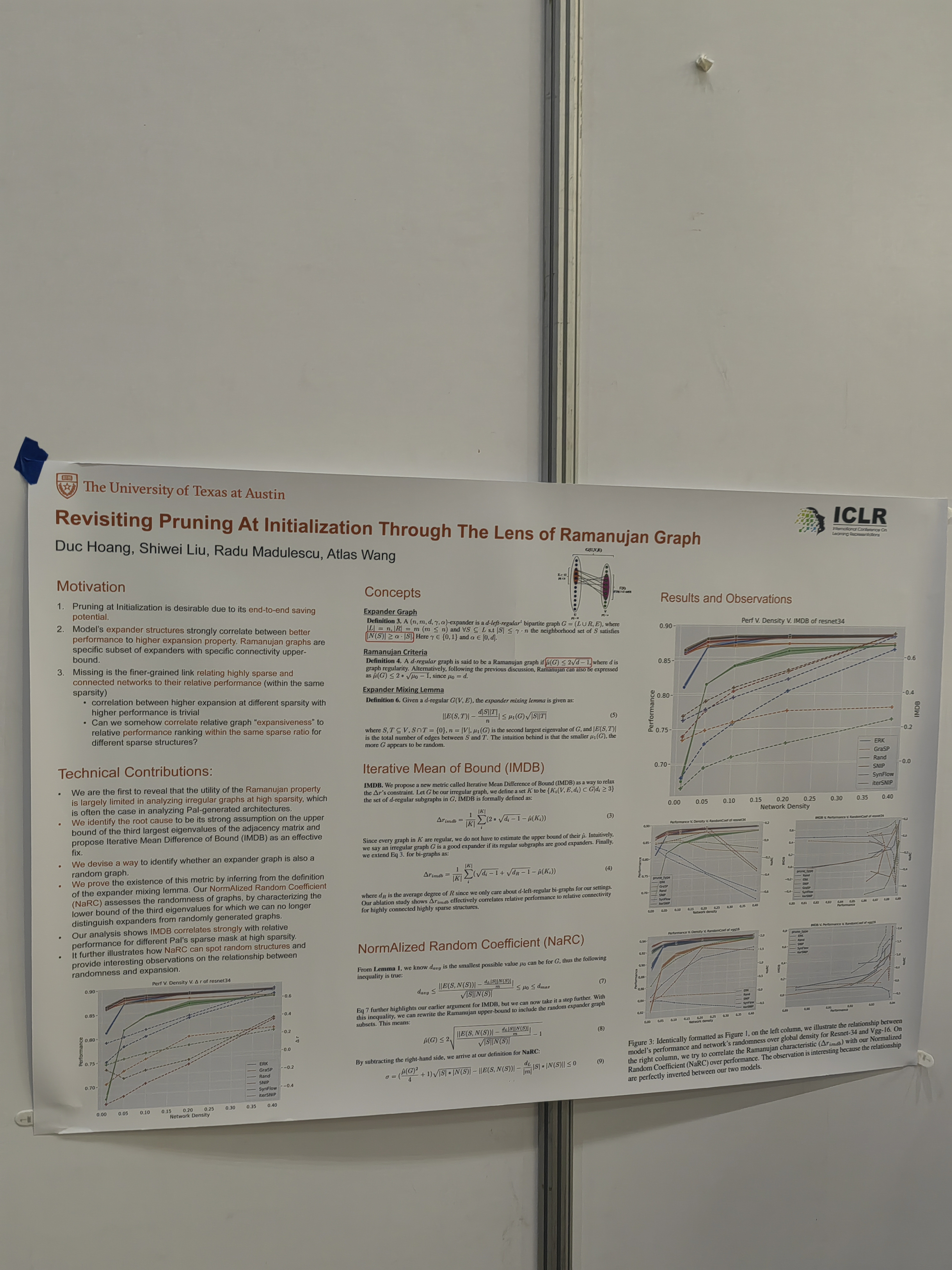
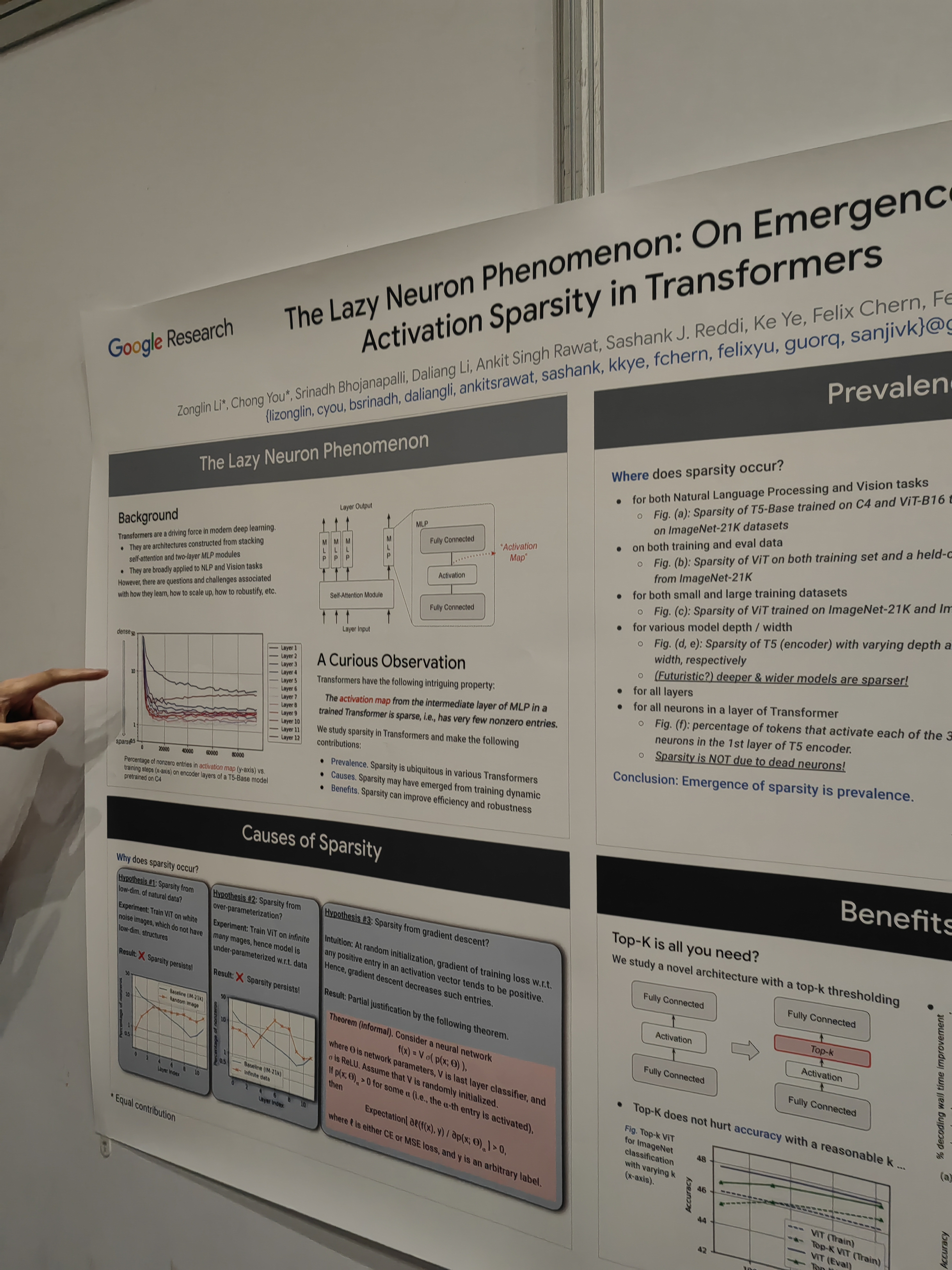
This work has been related to lottery ticket hypothesis. Sparsity of learned representation has been the subject of several talks.